Published on : 3rd Oct 2021

Advanced pointer in C programming #pointer
Pointer arithmetic :
Let say p is an pointer of type integer which stores the address of an integer type variable a.
int *p = &a;
if &a = 1000, then p = 1000.
Now p = p + 1 = 1000 + 1 * sizeof(int) = 1000 + 1 * 4 = 1000 + 4 = 1004
Similarly, p = p + 2 = 1000 + 2 * sizeof(int) = 1000 + 2 * 4 = 1000 + 8 = 1008
Formula :
if type *p, then p = p + n = p + n * sizeof(type). Here, n is an integer.
An array is nothing but a pointer. :
In pointer post, I have said that an array is nothing but a pointer. Array variable stores the base address of an array.
Let arr be an array.
int arr[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
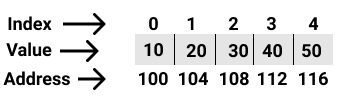
Let's discuss how subscript operator ([]) works.
arr[0] = *(arr + 0)
arr[1] = *(arr + 1)
.
.
arr[n] = *(arr + n)
Note : * is value at address operator. Example : *100 = 10(Pronounce is as value at address 100 is 10.), *112 = 40.
Now, arr = 100
So, arr[0] = *(arr + 0) = *(100 + 0) => *(100 + 0 * sizeof(int)) = *(100 + 0) = *100 = 10
Similarly, arr[1] = *(arr + 1) = *(100 + 1) => *(100 + 1 * sizeof(int)) = *(100 + 1 * 4) = *(100 + 4) = *104 = 20
Pointer of a pointer :
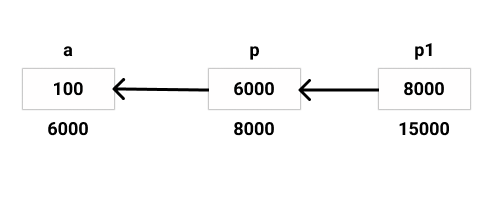
Let p be a pointer of type integer which stores the address of an integer type variable a. Let p1 be another pointer which stores the addres of pointer p.
So, p1 is called pointer of a pointer.
Syntax :
int *a = 10;
int *p = &a;
int **p1 = &p;
Similarly, we can have pointer to a pointer to a pointer and so on.
Source Code :
#include <stdio.h> int main(int argc, char** argv) { int a = 10; int *p = &a; int **p1 = &p; printf("Address of p = %u\n", &p); printf("Value of p1 = %u\n", p1); return 0; }
Output :
Address of p = 6487560 Value of p1 = 6487560
Null pointer :
When a pointer stores null value, it is called null pointer.
Example :
int *p = 0;
Void pointer :
A void pointer is a pointer which can store the address of variable of any data type.
Example:
int a = 10;
void *p = &a;